Microsoft Azure Prompt Flow · 2023 · B2B ToolingWhen AI workflows are script-heavy, iteration breaks at scale
Led end-to-end design of Prompt Flow’s visual system: Author → Evaluate → Compare.
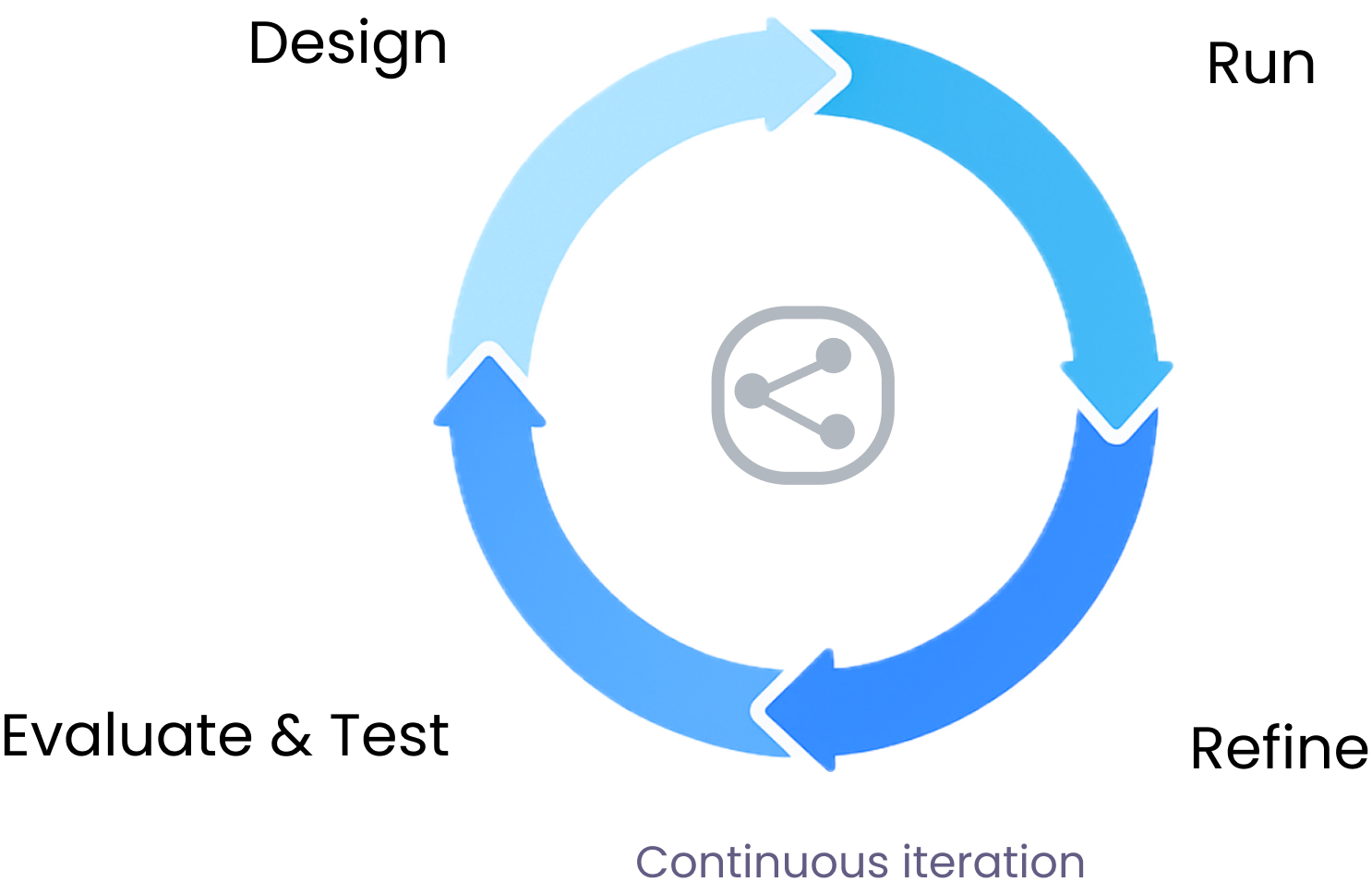
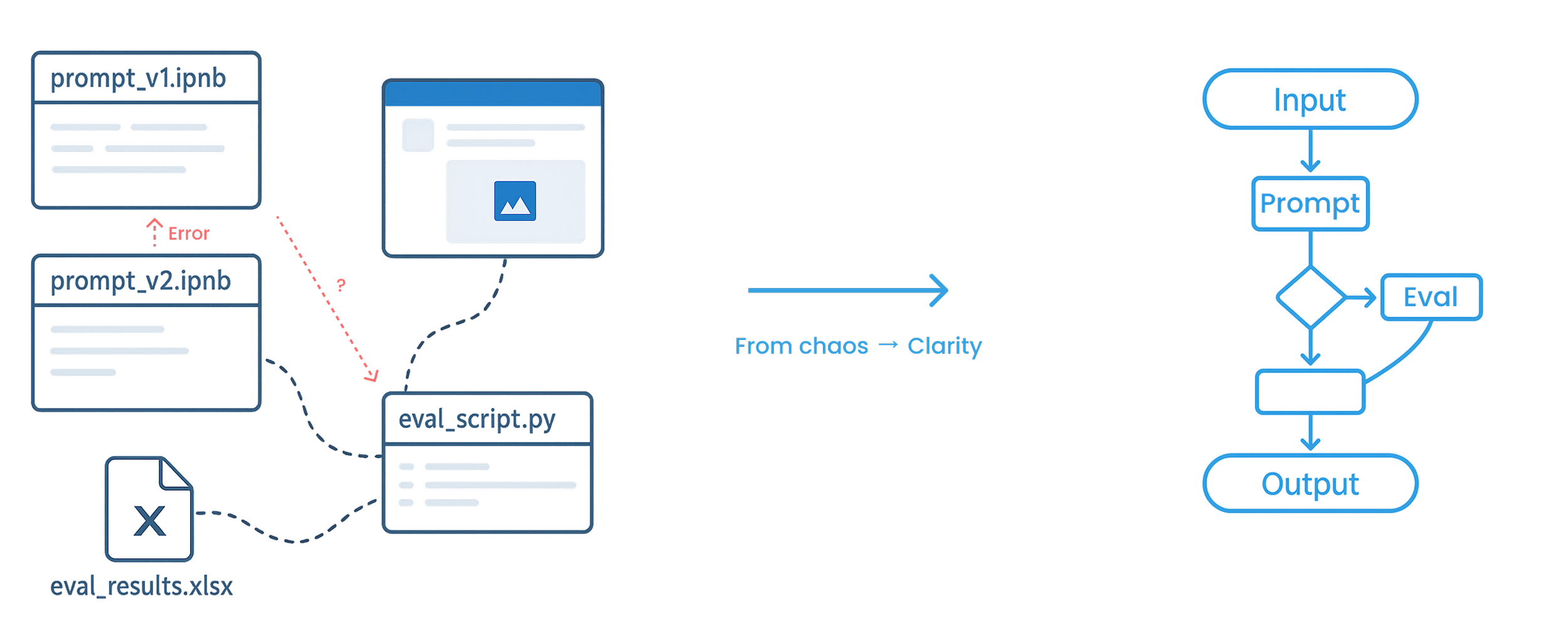
Key shift: from scattered scripts & tools → one continuous build → test → compare loop.
Demo: build → test → compare without leaving the editor
3x faster iteration
(integrated bulk test + eval in-flow)
20% Less setup overhead
(unified configuration + fewer context switches)
Adopted as a standard workflow pattern
(rolled into Azure AI tooling)
THE CHALLENGE
The Complexity of Scaling AI Workflows
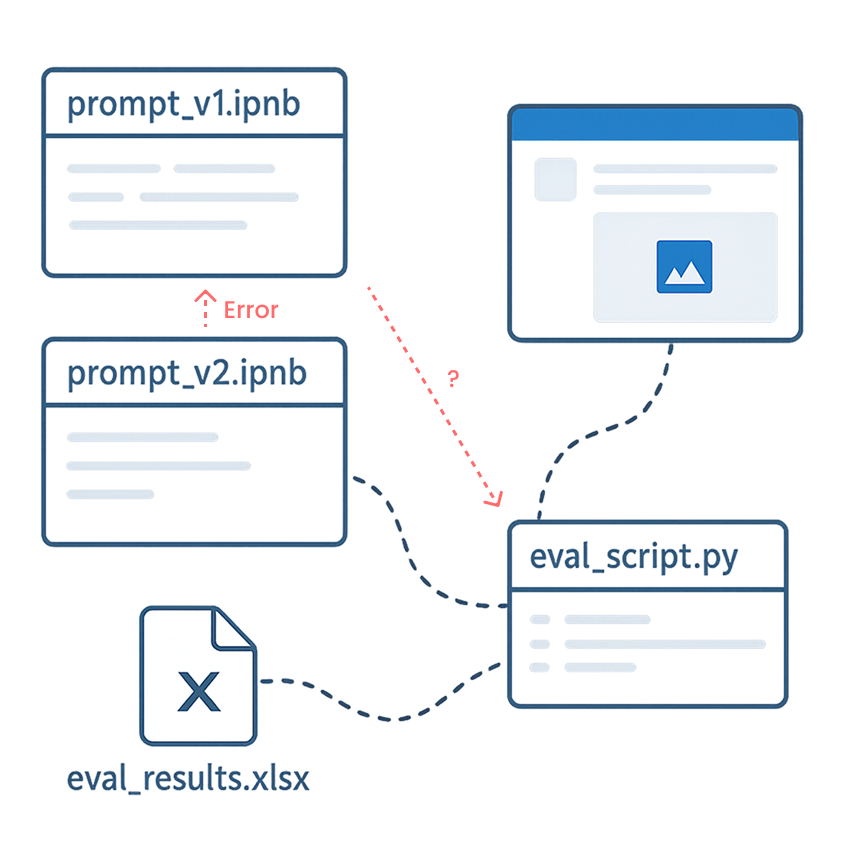
Iterative but Fragmented: Prompt engineering evolves through constant iteration—but rarely in one place.
The Visibility Gap: Scripts, notebooks, and configs scatter decisions into a black box.
At scale, AI workflows fail not because of model quality,
but because iteration becomes invisible and unmanageable.
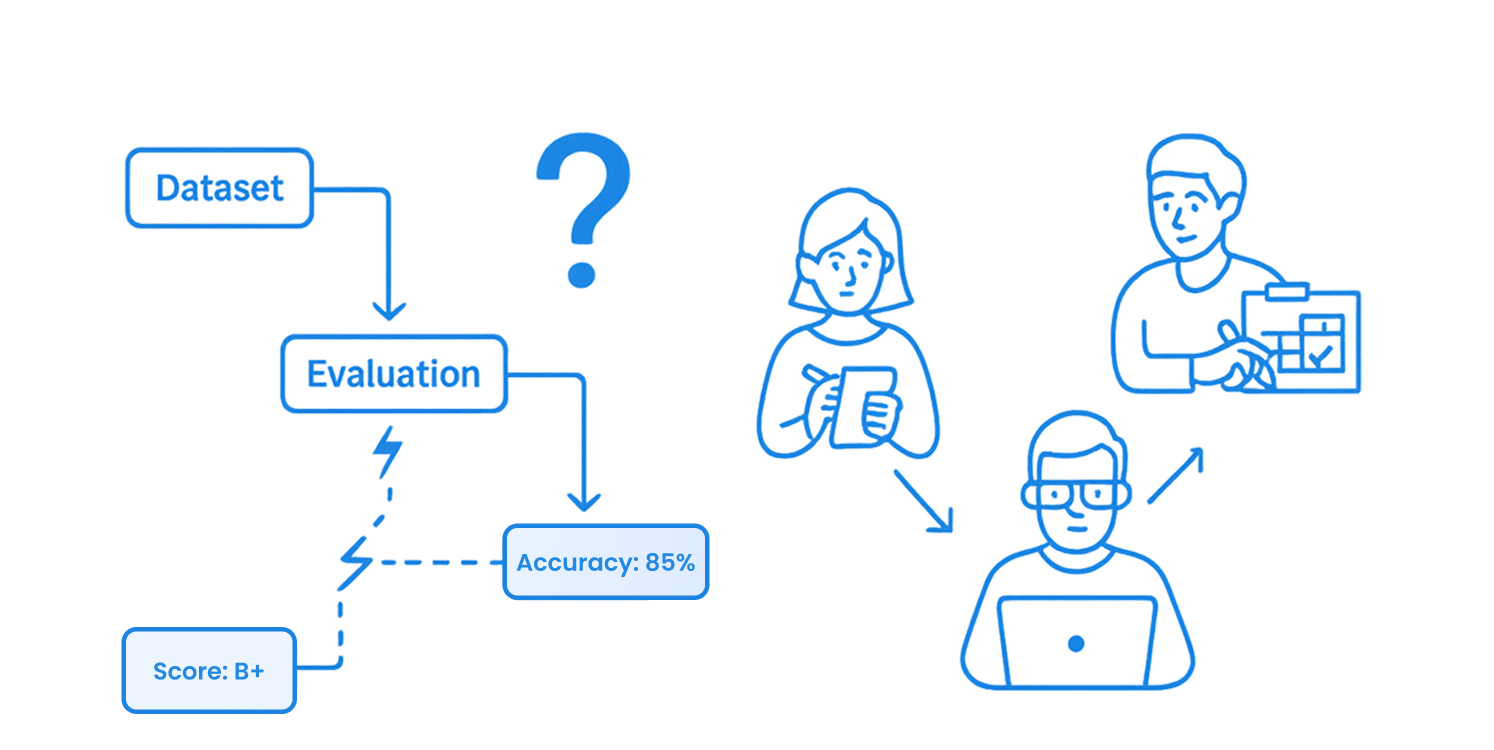
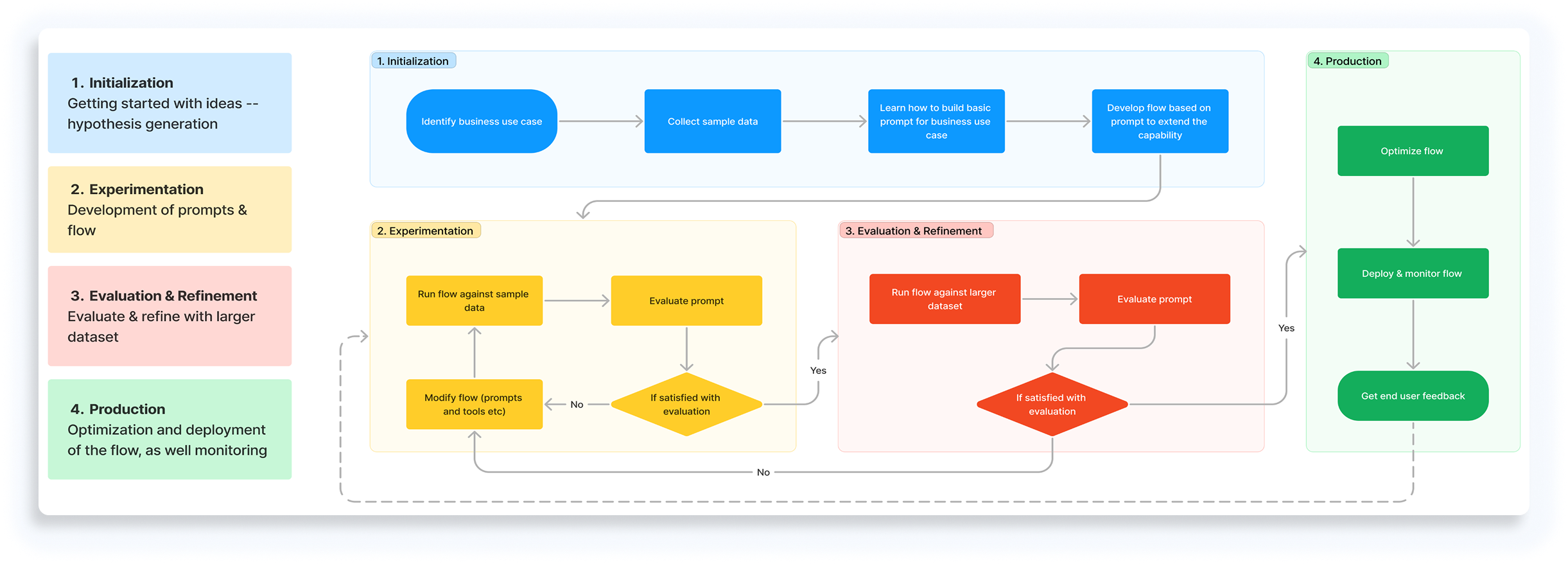
The standard AI lifecycle:
A loop that becomes unmanageable when scaled across cross-functional teams.
THE STAKEHOLDERS
Who feels the pain?
AI Engineers
Struggling with complex DAG logic.
Data Scientists
Lacking systematic evaluation tools.
Product Managers
Having zero visibility into prompt performance.
BREAKDOWN
Understanding the Problem Space
Why Existing AI Tooling Fails in Practice?
Evidence-Based Insights
12 Product Logs Analyzed (To understand behavioral patterns)
8 Expert Interviews (In-depth 1:1 sessions with DS & Engineers)
5 Contextual Inquiries (Observing real-world AI development workflows)
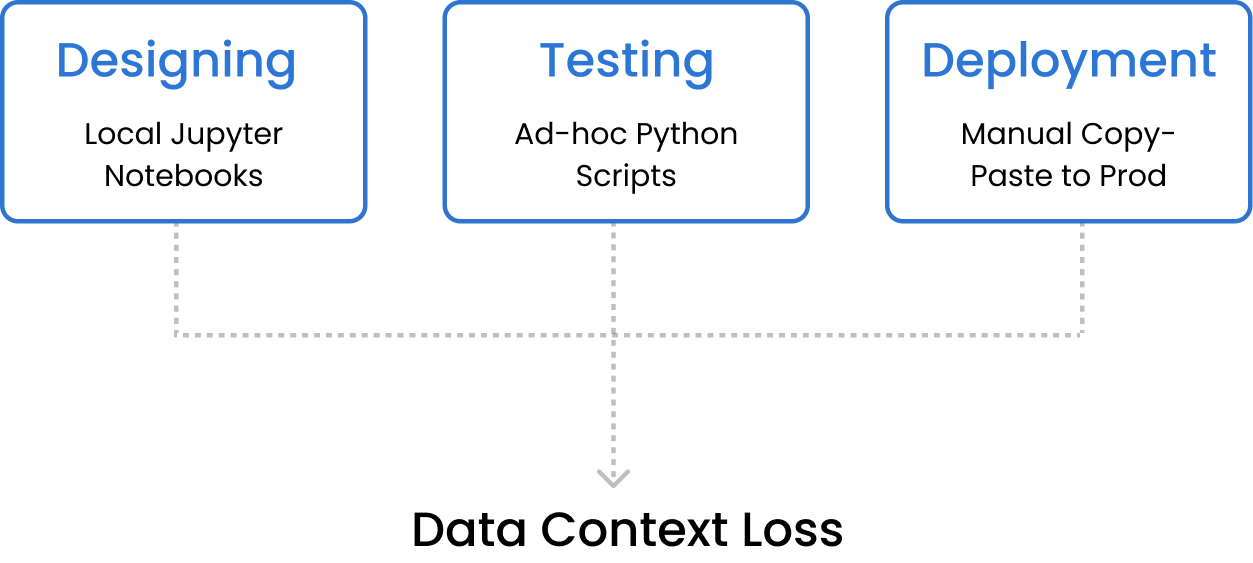
Fragmented Workflow
Design lives in Jupyter or local notebooks
Evaluation relies on ad-hoc scripts or manual scoring
Deployment handled separately in production pipelines
Result: workflows become manual, fragmented, and hard to reproduce.
The Tooling Gap: Usability vs. Control
Pros: Easy to start
Cons: Lacks Engineering Rigor, Subjective Evaluation Only
Pros: Flexible for developers
Cons: Siloed Environment, Reproducibility Challenges
Result: No tool today connects design, evaluation, and deployment into a single, shared workflow.
VALIDATION
3 Core Pain Points
Invisible Logic
Hard to trace or debug complex execution flows buried in scattered code scripts.
Unscalable Quality
Manual, one-off testing fails to provide systematic metrics across datasets at scale.
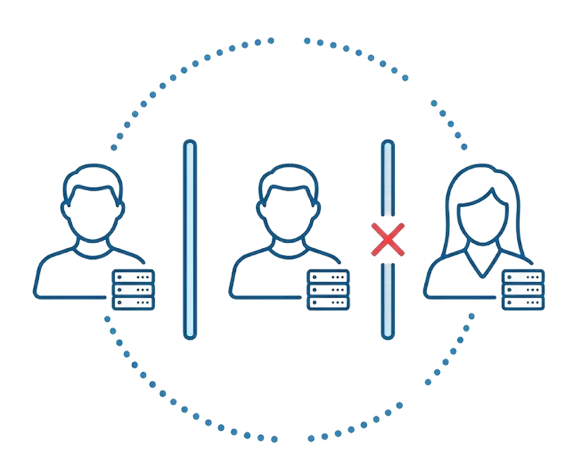
Siloed Handoffs
Significant friction between roles due to the lack of a shared visual workspace.
How might we transform fragmented prompt experiments into a visible, evaluable, and shareable workflow system that scales across teams?
DESIGN STRATEGY
The Visual DAG
Core Strategy
Represent prompt workflows as first-class, visual system objects — not hidden code.
By modeling workflows as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), execution logic becomes explicit, traceable, and reusable. This shared structure enables consistent evaluation, reliable collaboration, and scalable deployment across teams.
Why This Matters
SOLUTION 1
Making Prompt Logic Visible
Turn invisible execution into a visible workflow.
A visual editor that exposes prompt execution as a structured flow—so teams can understand, debug, and iterate with confidence.
DAG-based workflow model
Graph-based workflow view
Node-level inspection
Inline testing
SOLUTION 2
Unified Evaluation Flow
From subjective testing to consistent results.
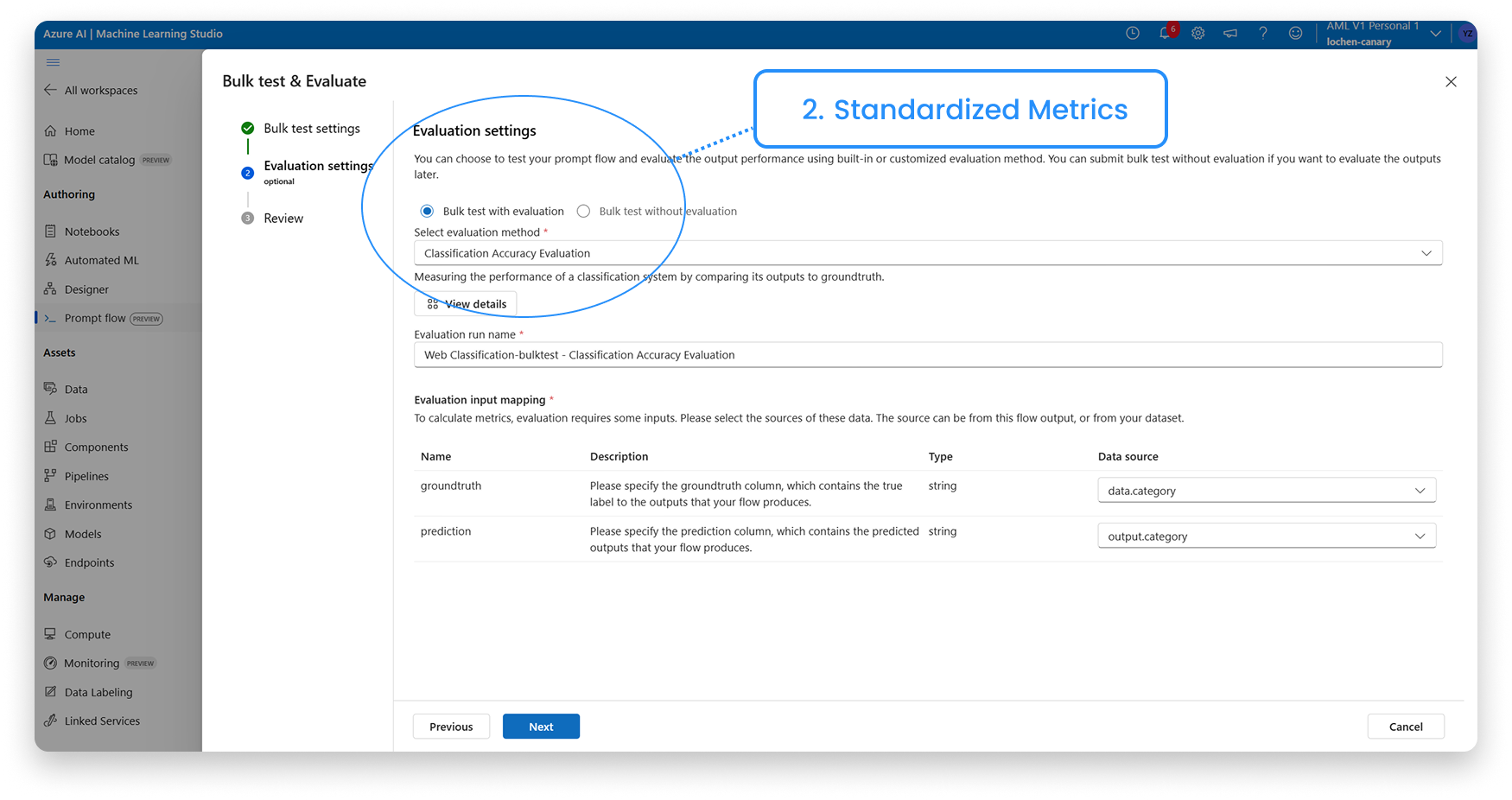
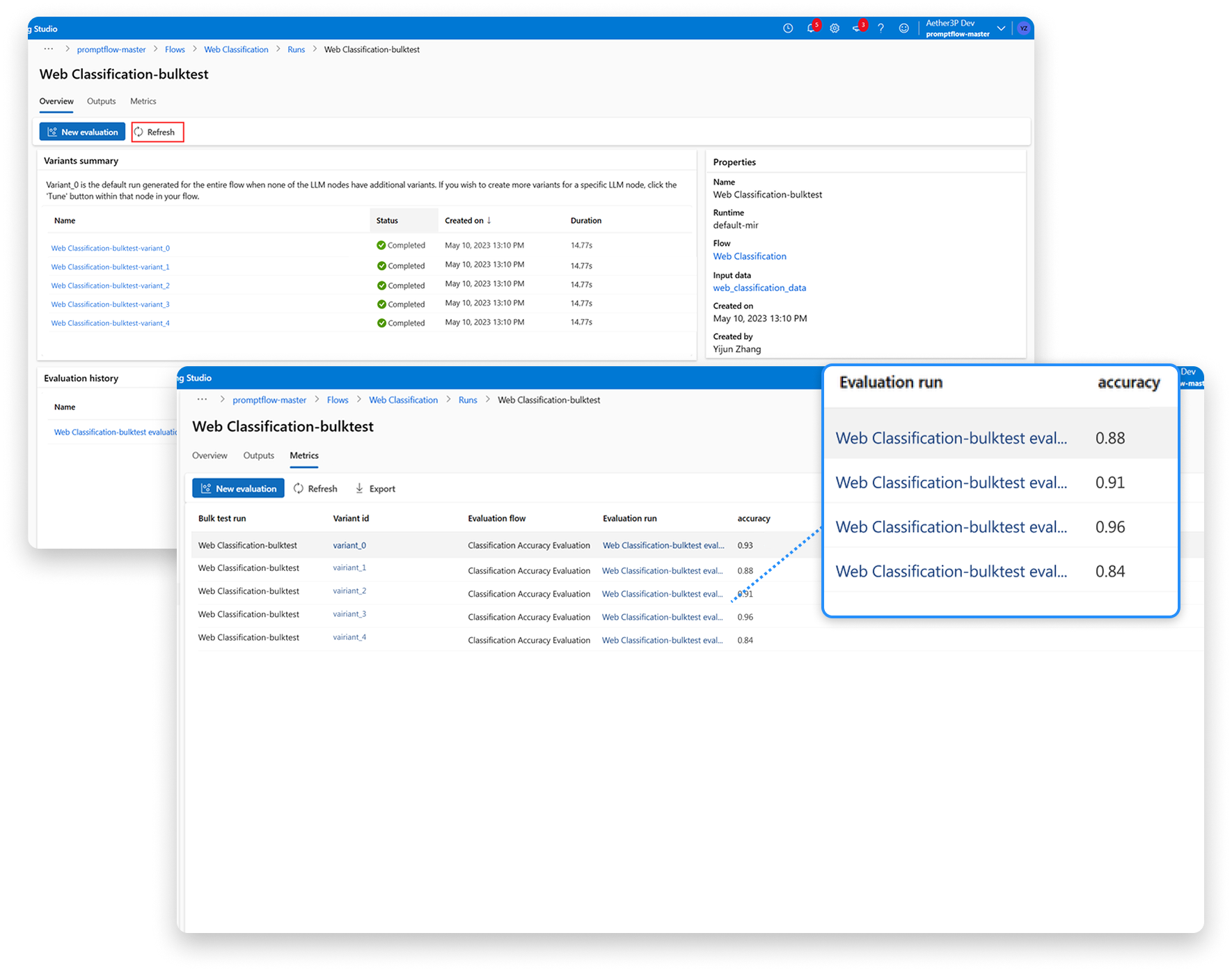
A centralized evaluation flow that enables bulk testing, standardized metrics, and side-by-side comparison.
1. Run large-scale prompt tests
3. Compare the Metrics
Evaluation runs on the same underlying workflow model
SOLUTION 3
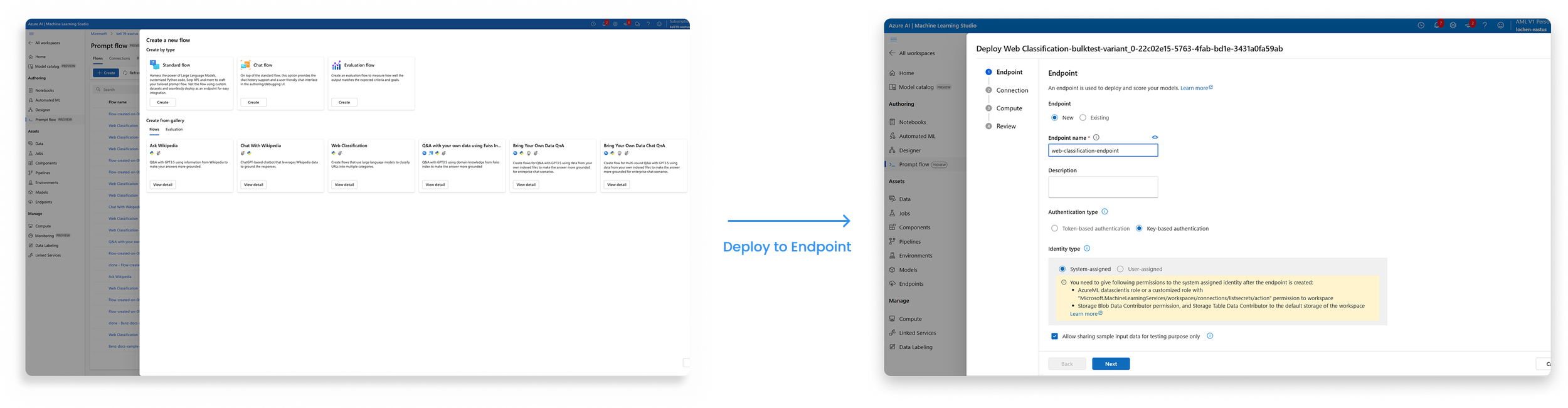
Collaboration & Deployment
From handoffs to continuity
A centralized evaluation flow that enables bulk testing, standardized metrics, and side-by-side comparison.
Shared flow gallery
One-click deployment
Design, evaluation, and deployment stay connected
EXPLORATION
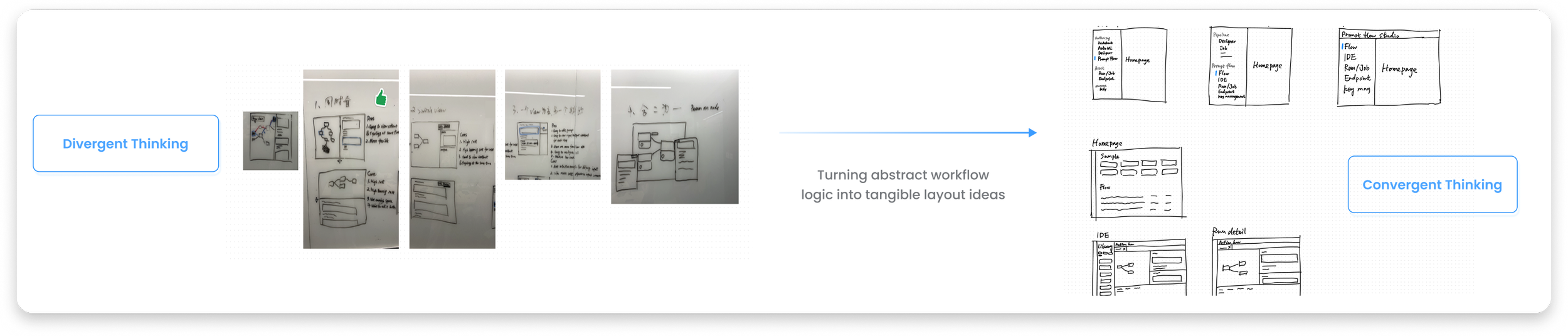
User Flow & Early Wireframe
Resolving system complexity before committing to UI Decisions
Defining the ideal workflow across experimentation, evaluation, and production.
From Abstract Logic to Tangible Interfaces
EXPLORATION
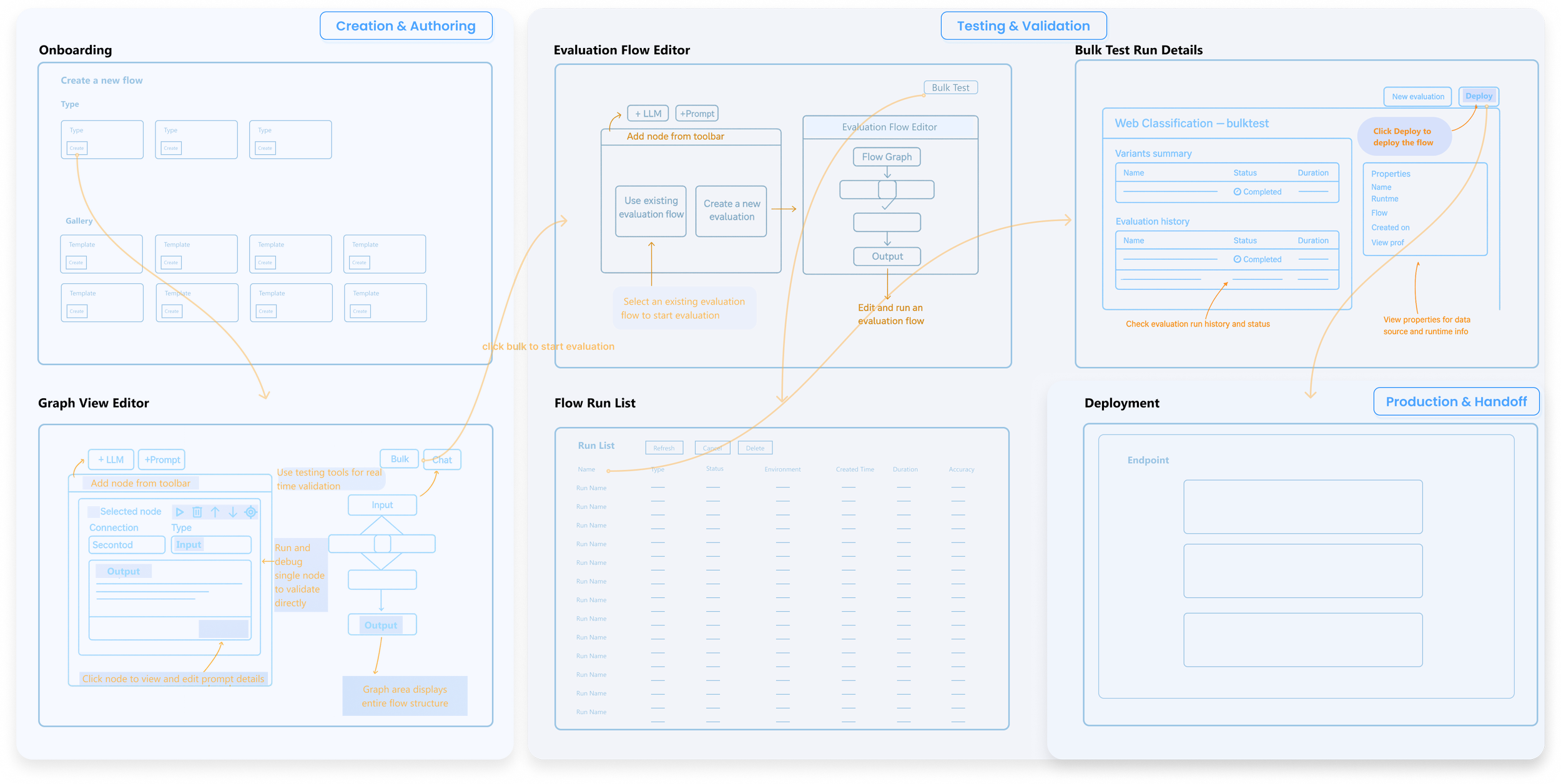
System Architecture & Navigation Model
A unified system that supports authoring, evaluation, and production handoff.
Highlighted paths show the most common authoring → evaluation → deployment flow.
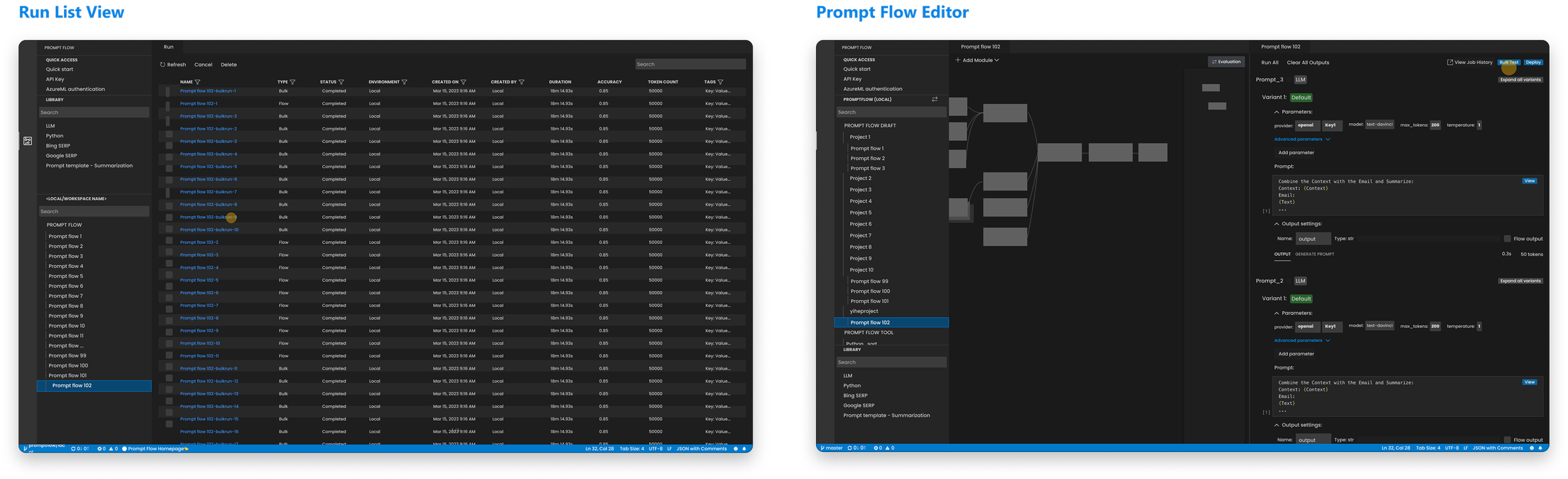
Early Validation in a Code - Centric Environment
Key Insight
Code-centric workflows scaled execution, but collapsed collaboration. They worked for individual engineers — and failed across roles.
This limitation led us to design a shared, visual workflow in Azure ML Studio.
ITERATION
Improving Graph & Node Readability
As flows grew larger, readability — not functionality — became the primary bottleneck.
Before
After
1. Fragmented execution context → Unified into a single flow
2. Panel-dependent understanding → Flow-first layout
3. Flat visual hierarchy → Clear node hierachy
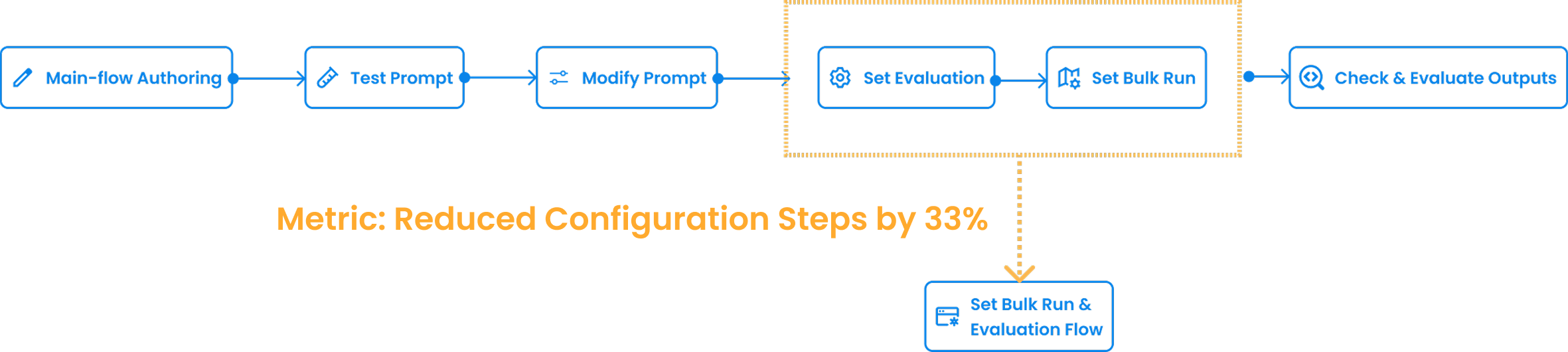
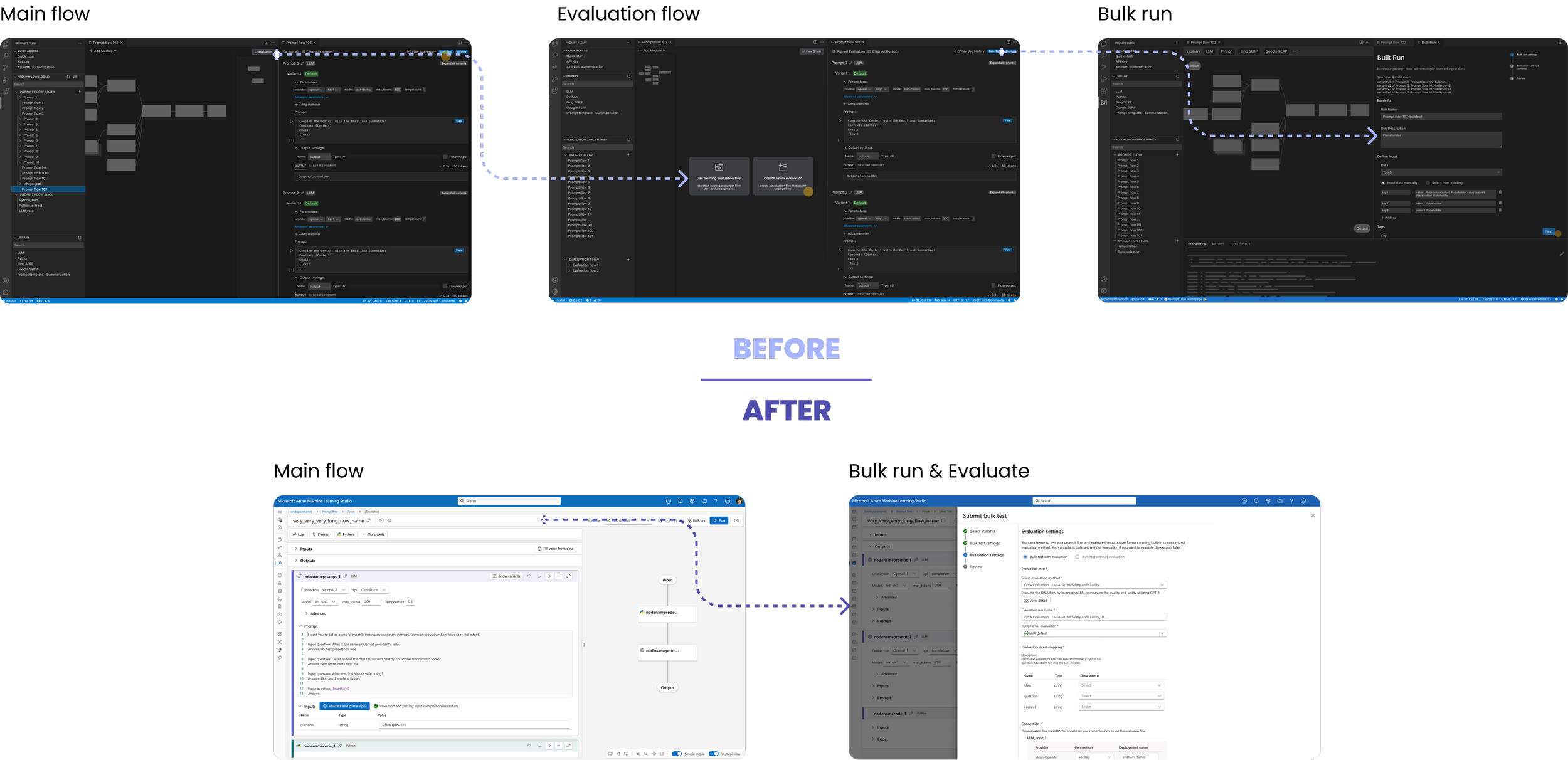
ITERATION
Integrating Evaluation Flow
Before: Separate setup for Bulk Run and Evaluation
After: Unified configuration —— less switching, faster testing
ITERATION
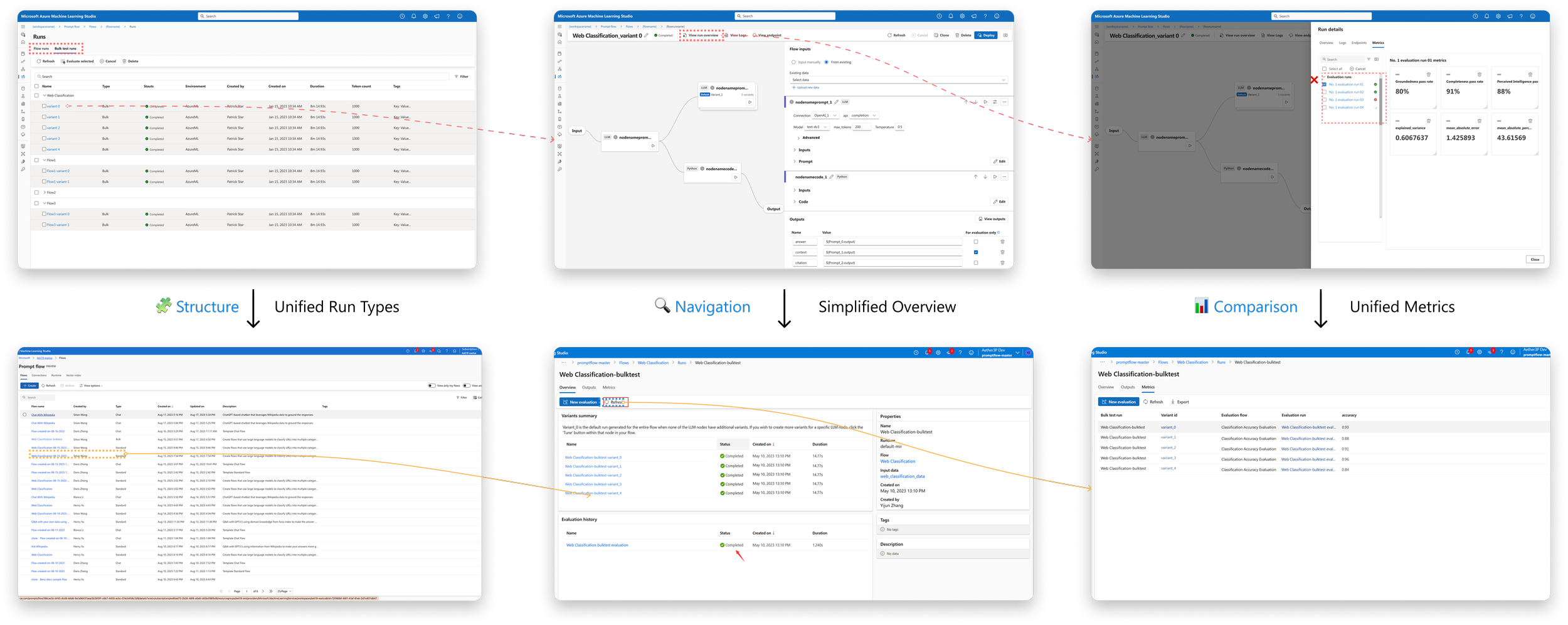
Unifying the “View Result” Flow for Multi-Variant Evaluation
Iteration Focus: Turning fragmented evaluation results into a first-class, comparable system object.
Before
After
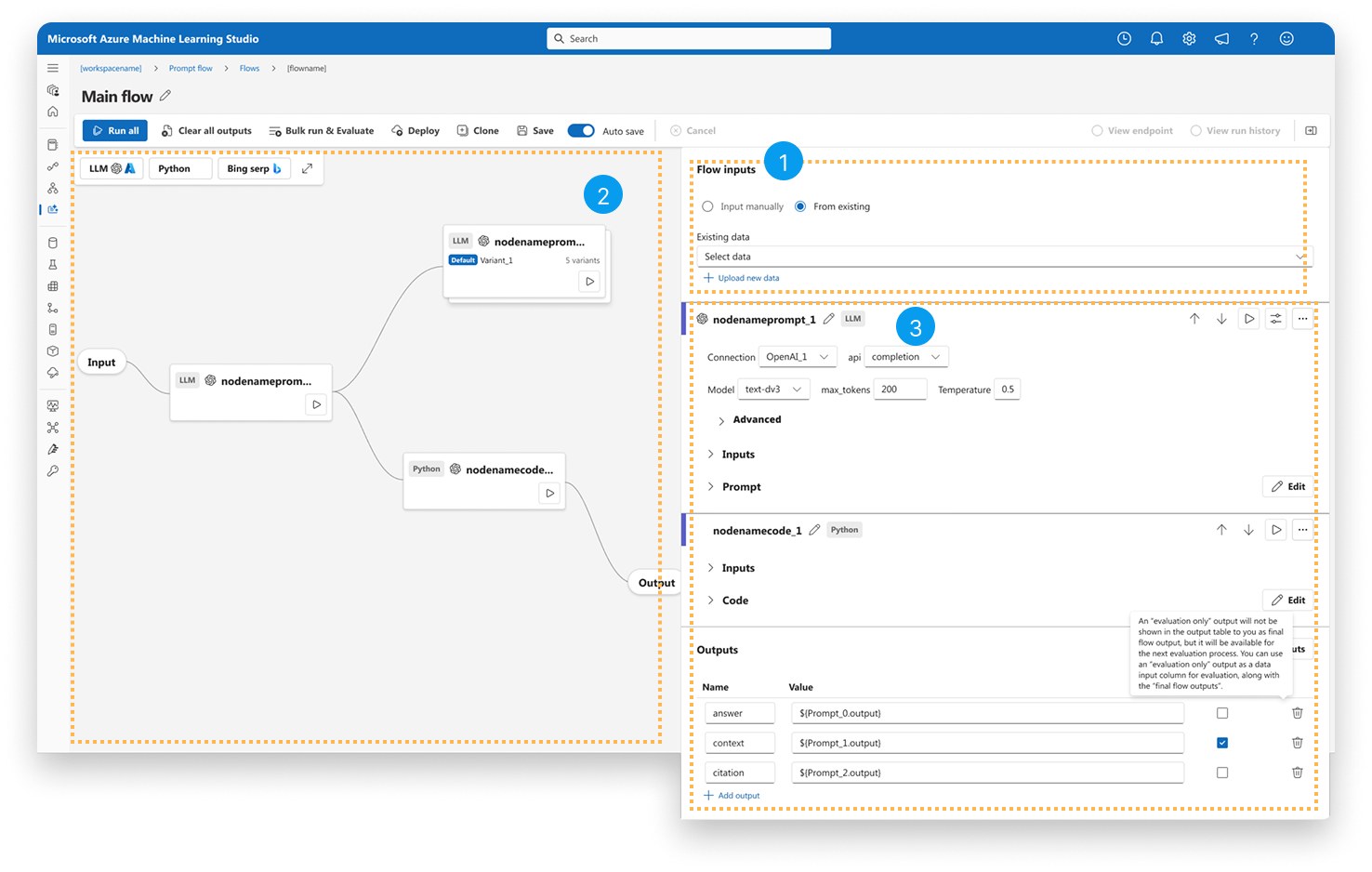
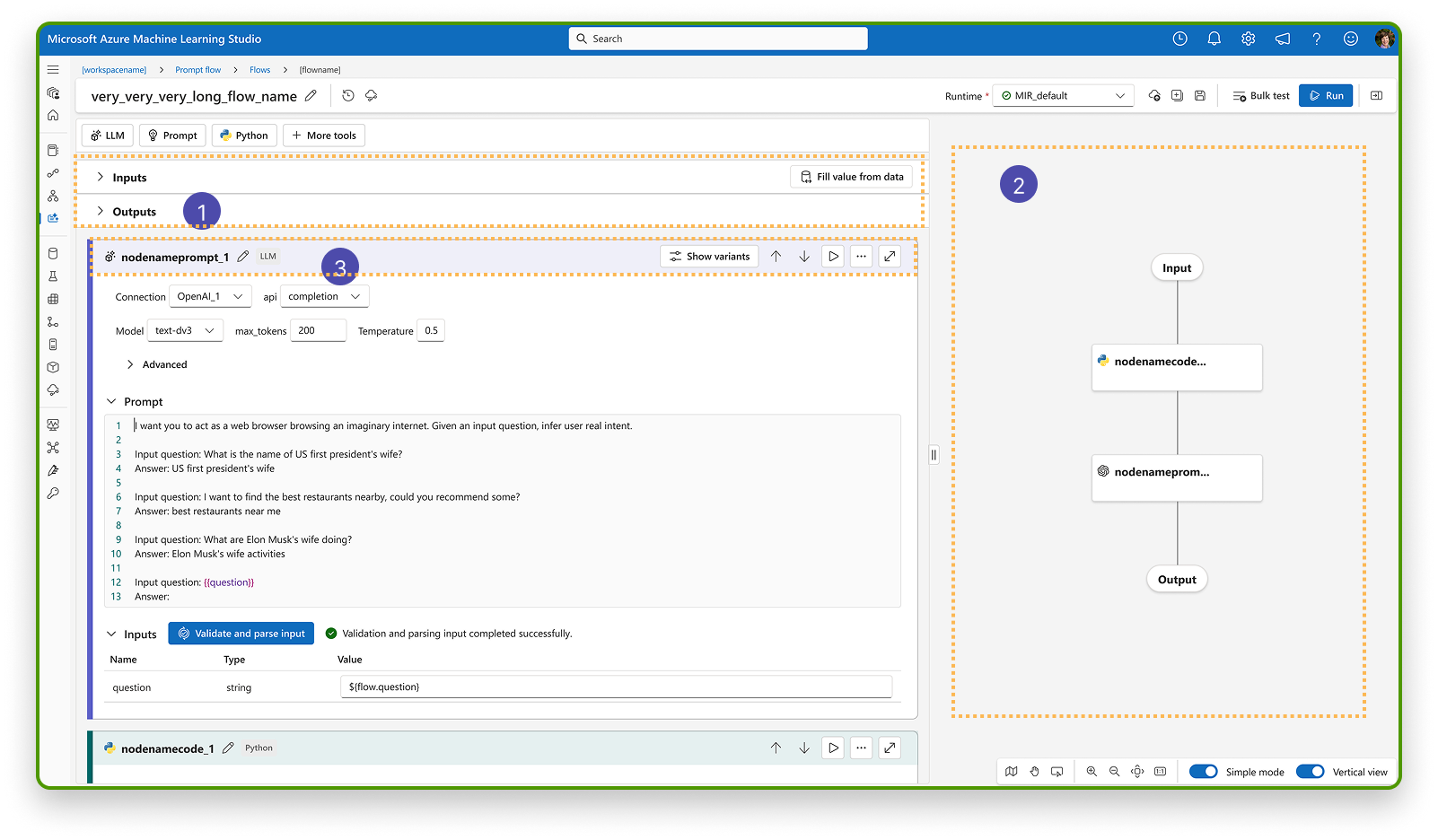
Visual Prompt Flow Editor
FINAL DESIGN
Unified authoring interface with inline configuration and visualized node status, improving clarity and iteration speed.
Evaluation & Result Review
FINAL DESIGN
Watch the seamless flow: triggering a bulk test directly from the authoring view in just 2 clicks.
Key Interaction Decisions
DESIGN DETAIL
Selective deep dives into critical interaction decisions that improved clarity and flexibility.
Detail 1 — Clear Input–Output Association
Problem
Multiple inputs made data flow hard to trace in complex nodes.
Decision
Enable linking directly from input fields to reveal data flow.
Detail 2 — No-Lock-in Authoring (Code-First Mode)
Problem
Advanced users preferred code-level control over visual-only editing.
Decision
Enable instant switching between visual and Python modes with full sync.
DESIGN ALIGNMENT
Adapting Fluent 2 for AI Workflows
Built on Fluent 2, we adapted supporting UI patterns to handle the density and interactivity required by AI workflow authoring.
Key Adaptation
High-density command surfaces
Adaptive panels for multi-context workflows
AI-specific interaction patterns
Outcome
High-density command surfaces
Adaptive panels for multi-context workflows
AI-specific interaction patterns
IMPACT
Impact & Adoption
Adopted as a standard workflow pattern
Used across Azure AI tooling for prompt authoring & evaluation.
3× faster iteration speed
Enabled by in-editor bulk testing and integrated evaluation flows.
~20% reduction in setup overhead
Fewer environment switches and unified configuration.
IMPACT
KEY Takeaways
Systems beat features
I learned that consistency is infrastructure — shared workflow logic matters more than isolated UI polish when scaling AI tools across teams.
Validation over speculation
High-fidelity prototypes aligned engineers faster than documentation or meetings, reducing decision risk early.
Design needs governance to scale
Design systems without contribution models eventually bottleneck teams — governance is a force multiplier, not overhead.